Further reading
Nappes to the north of the Rhone valley (in French)
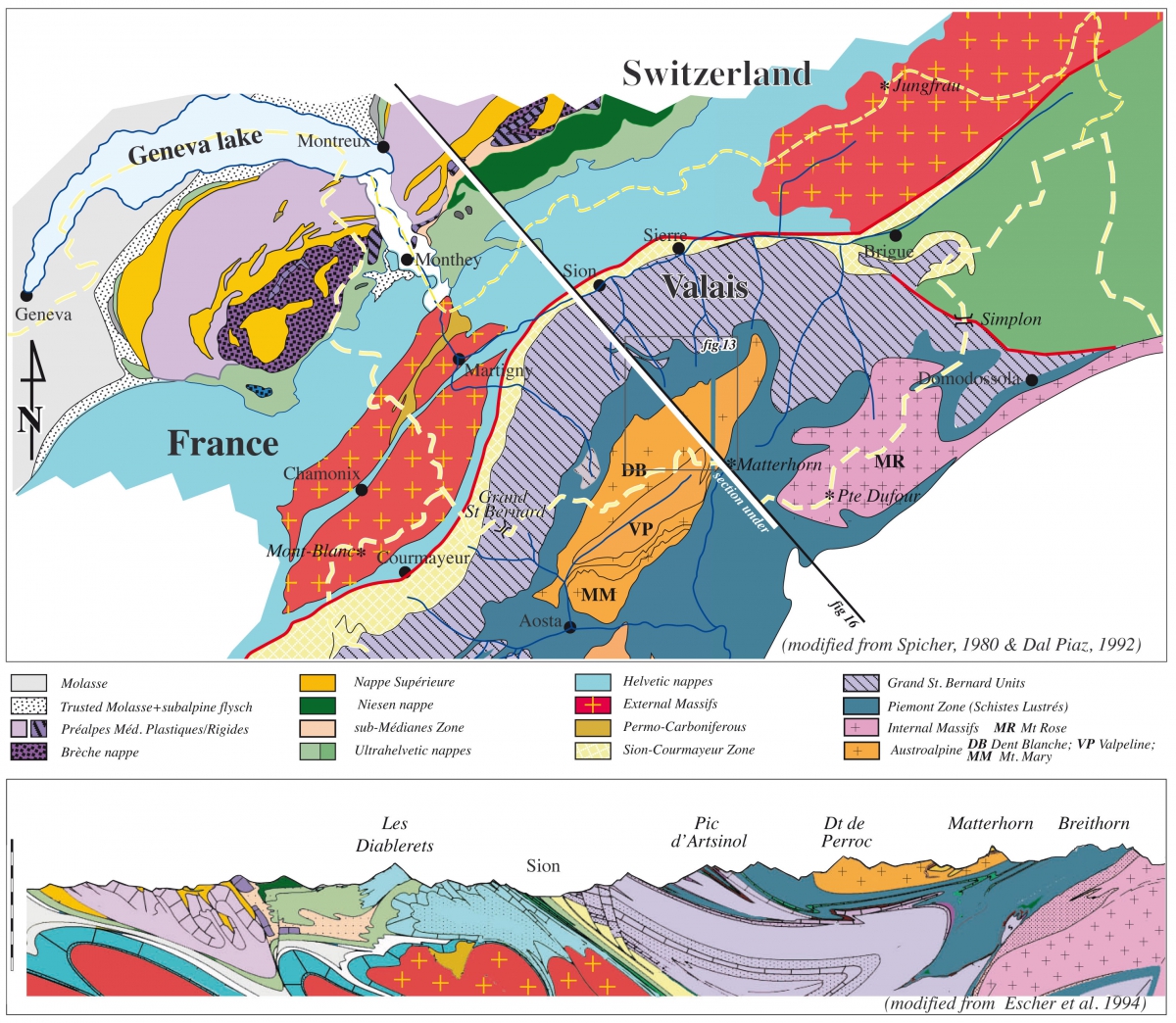
North of this zone the European continental margin domain is represented by the calcareous Helvetic nappes: the right bank of the Rhône River with limestone summits ranging from the Wildhorn up to the Dent de Morcles, and the left bank including the Dents du Midi. These sedimentary nappes were detached from their crystalline basement represented by the Variscan Mont-Blanc massif made of Carboniferous granite. This massif extends from the Mt Blanc in France to the Catogne in Valais, plunging under the Helvetic Nappes east of Martigny around Mont-Chemin,.
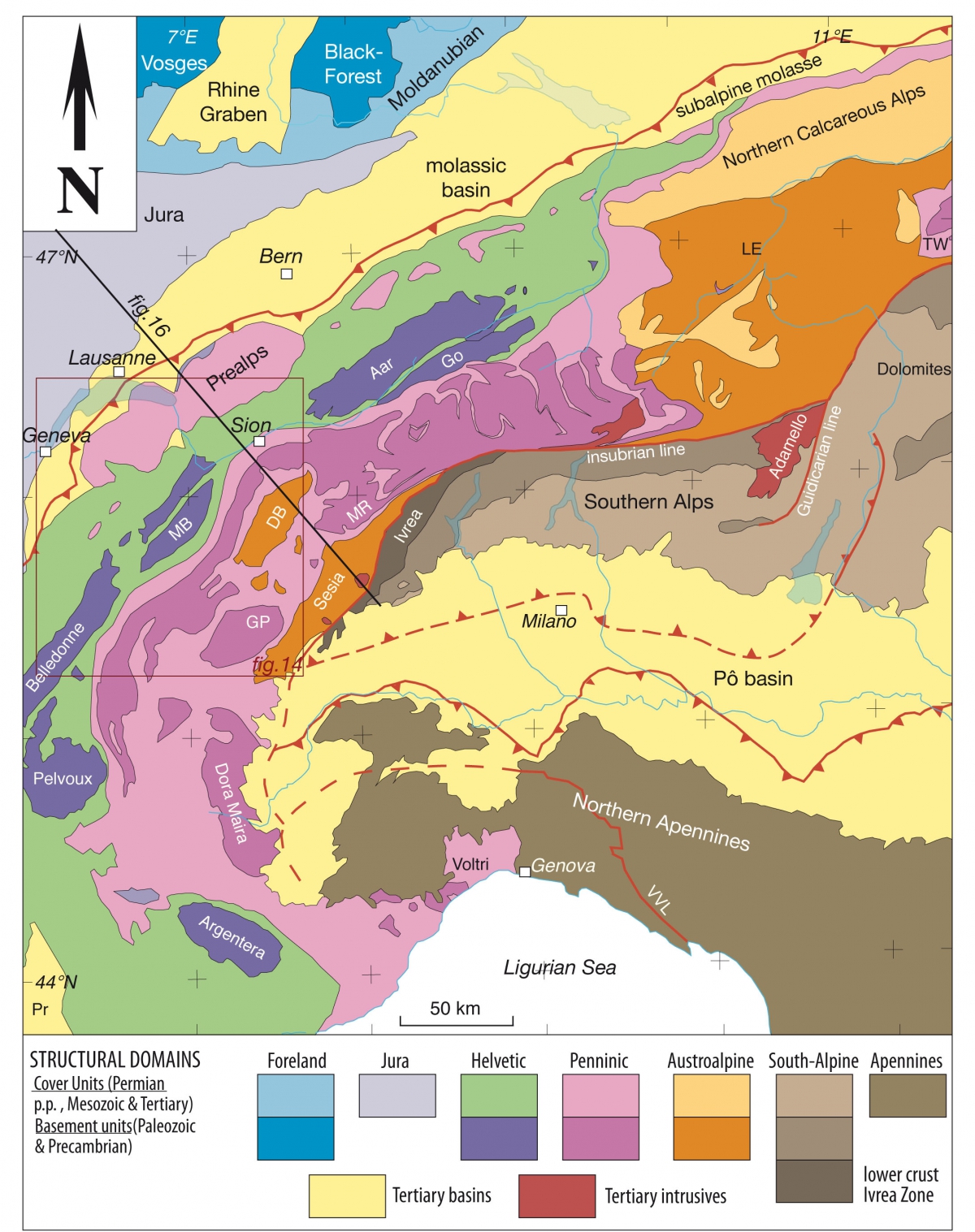
The large scale map shows the layout of different tectonic units.
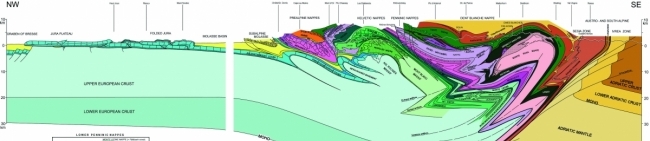
The cross-section of the entire alpine mountain belt also shows the Swiss Plateau, the molassic zone, and the Jura, the youngest part of the Alps folded 5 to 10 Ma ago. Southward through the Alps towards Italy, Aosta, are the Austroalpine Sesia zone, and the South-Alpine Ivrea zone – the western part of the Southern Alps representing the African plate.
The Dent-Blanche Nappe is called a klippe; it seems to float on the other nappes. It represents the western part of the large Austroalpine domain, well developed in Graubünden in Switzerland, and in Austria.